Crime data mining: A General Framework, and use in Indian Police Information System
Concern about national security has increased significantly since the terrorist attacks on 11 September 2001. The CIA, FBI, and other federal agencies are actively collecting domestic and foreign intelligence to prevent future attacks. Data mining applied in the context of law enforcement and intelligence analysis holds the promise of alleviating criminal and terrorist activities. Crime deterrence has become an upheaval tasks. The cops in their role to catch criminals are required to remain convincingly ahead in the eternal race between law breakers and law enforcers. The article highlights the existing systems used by Indian police as e-governance initiatives and also proposes an interactive query based interface as crime analysis tool to assist police in their activities.
Introduction
Data mining is a powerful tool that enables criminal investigators who may lack extensive training as data analysts to explore large databases quickly and efficiently[1]. Computers can process thousands of instructions in seconds, saving precious time. Computers are also less prone to errors than human investigators, especially those who work long hours. Intelligence agencies such as the CIA and FBI are actively collecting and analyzing information to investigate terrorists’ activities.
Police is a critical component of civil administration in India. Indian constitution assigns responsibility for maintaining law and order to the states and territories, and almost all routine policing, including apprehension of criminals, is carried out by state-level police forces. The police functioning have remained a constant area of governmental concern and efforts to improve it upon further and further. The exchange of information among police agencies has become very time consuming.
A criminal act can encompass a wide range of activities, from civil infractions such as illegal parking to internationally organized mass murder such as the 9/11 attacks. Law-enforcement agencies across the US compile crime statistics using well-established standards such as the FBI’s Uniform Crime Reporting System and its successor, the National Incident-Based Reporting System as well as other criteria defined by jurisdictional needs and requirements. Some such as traffic violations and arson, concern police at the city, county, and state levels [2].
Overview of Crime Data Mining and its Techniques
Crime Types and Security Concerns
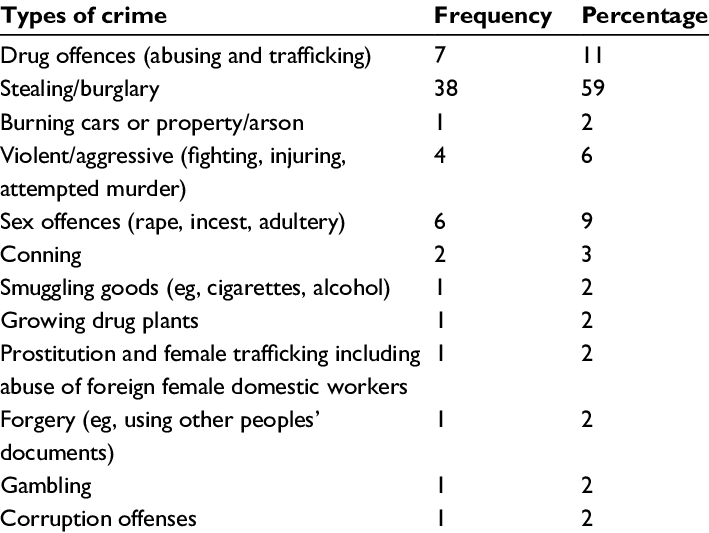
Table summarizes the different types of crimes in increasing degree of public influence[3]
Crime Data Mining Framework[4]
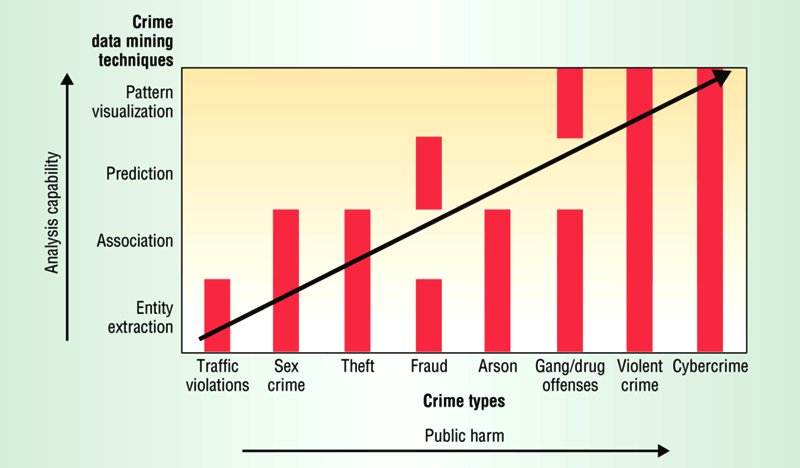
The framework identifies relationships between techniques applied in criminal and intelligence analysis at the local, national, and international levels.
Crime Data Mining for Indian Police Information System [5]
Role of Indian Police
The major existing roles of police are prevention of criminality, repression of crime, apprehension of offenders, regulation of non-crime conduct and recovery of stolen property etc.
The National Crime Record Bureau has developed following e-governance applications systems:
• Police Station Management System
• Prison Statistics
• Jail Management Softwares.
• Prosecution Branch System
• National Bomb Squad System and Forensic Science Laboratory System.
Existing Indian Police Information Systems: Crime Criminal Information System (CCIS)
CCIS is a national project of sharable database on crime and criminals at district, state and national level for assisting investigating and supervising officers and police planners to formulate crime-control strategies.
The main objective of the CCIS is to[6]
• Computerize crime and criminal information collected by Inquiry Officer
• Link a crime to criminal and property • Link a criminal to crime • Link a property to crime
• Generate vital reports from database • Reduce manual effort and increase efficiency of police
Concluding Remarks
Crime association and clustering techniques can reveal the identities of cyber criminals who use the Internet to spread illegal messages or malicious code. Investigators can use machine-learning algorithms—such as ID3, neural networks, Support Vector Machines, and genetic algorithms—to predict crimes by analyzing factors such as time, location, vehicle, address, physical characteristics, and property. Crime data mining has a promising future for increasing the effectiveness and efficiency of criminal and intelligence analysis. Many future directions can be explored in this still young field. For example, more visual and intuitive criminal and intelligence investigation techniques can be developed for crime pattern and network visualization. Crime analysis tool will provide an upper edge and with the use of the crime analysis tool policing can be made effective, fast and responsible in their operation.
REFERENCES
[1]. U.M. Fayyad and R. Uthurusamy, “Evolving Data Mining into Solutions for Insights,” Comm. ACM, Aug. 2002, pp. 28’-31.
[2]. W. Chang et al., “An International Perspective on Fighting Cybercrime,” Proc. 1st NSF/NIJ Symp. Intelligence and Security Informatics, LNCS 2665, Springer-Verlag, 2003, pp. 379-384.
[3].https://www.google.com/searchq=types+of+crime&sxsrf=ALeKk00h26_XxNCJs8BtH6b6qrXCcHTtJA:1598938334584&source=lnms&tbm=isch&sa=X&ved=2ahUKEwjC_cy7ncfrAhUq8AKHUXbDAQQ_AUoAnoECA4QBA&biw=1366&bih=625#imgrc=qLT1E_DBV_T7KM.
[4].https://www.google.com/searchq=crime+data+mining+framework&sxsrf=ALeKk00_E0QNlT6_OO8M2zvoB1zKJZ6vA:1598938734521&source=lnms&tbm=isch&sa=X&ved=2ahUKEwi0m6f6nsfrAhVT6uAKHfsVC5YQ_AUoAXoECA0QAw&biw=1366&bih=576#imgrc=8__HNIiTaLPV6M.
[5]. Manish Gupta*, B. Chandra and M. P. Gupta Crime Data Mining for Indian Police Information System.
[6]. https://www.mha.gov.in/division_of_mha/centre-state-division/national-crime-records-bureau-iso-90012000-organisation.
Written By :- Assistant Professor Shruti Bhalla
